AMSAT OSCAR 7 (AO-7)
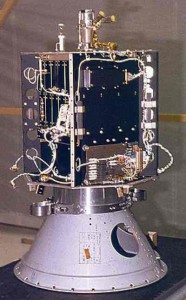 AO-7 (aka AMSAT-OSCAR 7) is the second Phase 2 amateur satellite launched into Low Earth Orbit on 15 November 1974. It remained operational until a battery failure in 1981. On 21 June 2002 the satellite was heard again on its 2 meter beacon (145.9775 MHz CW) after 21 years of silence, and 27 years in space. AMSAT reported AO-7 still semi-operational on 6 April 2006, with reliable power only from its solar panels; the report stated the cause of the outage was a short circuit in a battery and the restoration of service was due to its becoming an open circuit. The satellite eclipses on every orbit during the northern summer and autumn; the rest of the year it is in continuous sunlight and alternates between transmission modes A and B.
AO-7 (aka AMSAT-OSCAR 7) is the second Phase 2 amateur satellite launched into Low Earth Orbit on 15 November 1974. It remained operational until a battery failure in 1981. On 21 June 2002 the satellite was heard again on its 2 meter beacon (145.9775 MHz CW) after 21 years of silence, and 27 years in space. AMSAT reported AO-7 still semi-operational on 6 April 2006, with reliable power only from its solar panels; the report stated the cause of the outage was a short circuit in a battery and the restoration of service was due to its becoming an open circuit. The satellite eclipses on every orbit during the northern summer and autumn; the rest of the year it is in continuous sunlight and alternates between transmission modes A and B.
Two types of communications repeaters are aboard the spacecraft, only one of which operates at a time. The first repeater is a higher power, two-watt version of the one-watt two-to-ten motor linear repeater that flow on the OSCAR 6 mission. This unit receives uplink signals between 145.85 and 145.95 MHz, and retransmits them between 29.4 mid 29.5 MHz an the downlink. A 200 milliwatt telemetry beacon provides telemetry data on 29.502 MHz.* Approximately -100 dBm is required at the repeater input terminals for an output of 1 watt. This corresponds to an eirp from the ground of 90 watts for a distance to the satellite of 2,000 miles and a polarization mismatch of 3 dB.
The second repeater, constructed by AMSAT Deutschland e.V., AMSAT’s affiliate in Marbach, West Germany, is a 40-kHz* bandwidth linear repeater. It employs an 8-watt PEP power amplifier using the envelope elimination and restoration technique to maintain linear operation over a wide dynamic range with high efficiency. This repeater has an uplink from 432.125 to 432.175 MHz, and a downlink from 145.925 to 145.975 MHz. Since the uplink band in shared with the radiolocation service, an experimental pulse suppression circuit is incorporated in the repeater to reduce the effects of wideband pulsed radar interference in the uplink. Developmental versions of this repeater have flown in high-altitude balloon experiments in Germany, and aircraft flight tests of the repeater prototype unit. A 200 milliwatt telemetry beacon on 145.975′ provides telemetry data. Approximately So W.*eirp is required to produce 3 watts of repeater output at a range of 2,000 miles assuming.& polarization mismatch of 3 db.
Orbital Parameter
Name AO-07 NORAD 07530 COSPAR designation 1974-089-B Inclination (degree) 101.619 RAAN 242.249 Eccentricity 0.0012444 ARGP 178.341 Orbit per day 12.53570748 Period 1h 54m 52s (114.87 Min) Semi-major axis 7828 km Perigee x apogee 1440 x 1459 km Drag factor 0.000100000 1/ER Mean anomaly 181.770
Downlink
29.400 – 29.500 MHz (USB) Mode A
145.925 – 145.975 MHz (USB) Mode B
Uplink
145.850 – 145.950 MHz (USB) Mode A
432.125 – 432.175 MHz (LSB) Mode B
Antenna polarisation
unknown
Status
Active
Callsign
W3OHI
Telemetry
Sometimes when the satellite is in mode B, the CW beacon is active on 435.106MHz. After the classical HI HI 24 telemetry channels follow.
hihi 100 175 173 176 257 201 242 253 368 304 343 339 434 435 448 448 531 507 540 557 610 643 601 651 hihi 100 176 173 177 252 201 242 252 366 387 342 339 435 434 449 448 531 508 540 558 613 645 601 651 hihi 100 167 177 175 255 201 242 253 367 311 342 339 435 434 448 448 530 507 540 559 607 640 601 651
Homepage and other references:
