KySat-2
 KySat-2 is the second satellite to be entirely designed, built, and tested by students of the University of Kentucky and Morehead University. Development of the satellite began in 2011, shortly after the launch of KySat-1
KySat-2 is the second satellite to be entirely designed, built, and tested by students of the University of Kentucky and Morehead University. Development of the satellite began in 2011, shortly after the launch of KySat-1
Mission
The primary objective of KySat-2 is proof of concept. Using lessons learned from KySat-1, SSL has spent the past two years designing, revising, and optimizing KySat-2. KySat-2 will demonstrate key technologies developed by University of Kentucky and Morehead University students. These include a distributed network computing architecture, power and radio systems, and a “stellar gyroscope” for attitude determination. If successful, KySat-2 will serve as a standard on which to base future satellites built by the lab.
- Stellar Gyroscope: KySat-2 will demonstrate the stellar gyroscope concept in orbit
- Passive Magnetic Stabilization: KySat-2 is equipped with a passive attitude control scheme known as Passive Magnetic Stabilization.
Orbital parameters
Name KySat-2 NORAD 39384 COSPAR designation 2013-064-E Inclination (degree) 40.499 RAAN 207.826 Eccentricity 0.0015695 ARGP 253.163 Orbit per day 15.41349107 Period 1h 33m 25s (93.42 min) Semi-major axis 6 820 km Perigee x apogee 431 x 453 km Drag factor 0.001472000 1/ER Mean Anomaly 106.806
Downlink
437.405 MHz 9600 FSK 1W output Beacon Period: 15-45 seconds
Uplink
Callsign
KK4AJJ
TLE
KySat-2 1 39384U 13064E 14271.14379904 .00063491 00000-0 14720-2 0 3592 2 39384 40.4992 207.8260 0015695 253.1627 106.8056 15.41349107 47837
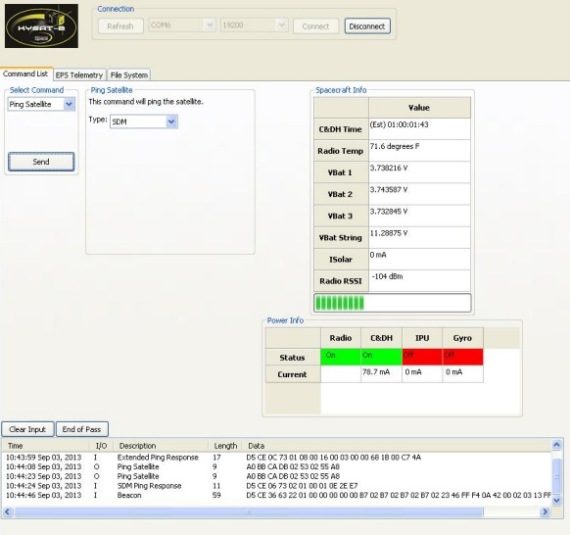
Telemetry
To help decode packets from KySat-2, we have developed software radio amateurs can download and install. Both are available here: Amateur-radio-operators
Status
Not active. Expected to be launched with Minotaur 1 ORS-3 at November 20th 00:30 UTC 2013.
Homepage and other references:
KySat-2 main website
